Eczema: Understanding Its Causes and How to Manage It Effectively
Eczema affects millions of people, often causing persistent itching, dryness, and irritation that can interfere with daily comfort. By gaining a clearer understanding of what contributes to this condition and exploring medically recommended ways to manage it, individuals can better support their skin’s health and improve their quality of life.
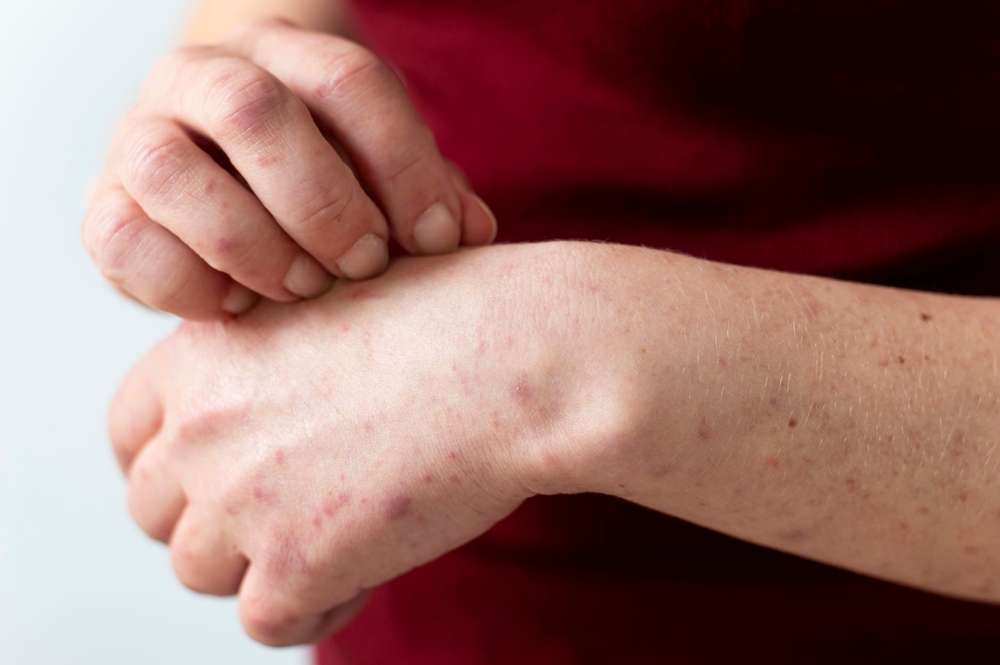
What are the most common internal triggers of eczema?
Internal triggers play a crucial role in eczema flare-ups. Genetics is a primary factor, with research showing that individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies are more likely to develop the condition. Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy or menstruation, can also trigger eczema symptoms in some people. Stress is another significant internal trigger, as it can weaken the skin barrier and increase inflammation. Additionally, certain foods may exacerbate eczema in some individuals, although this varies from person to person. Common food triggers include dairy, eggs, nuts, and gluten-containing grains.
What external factors commonly trigger eczema outbreaks?
External triggers are equally important in managing eczema. Environmental factors such as low humidity, extreme temperatures, and sudden temperature changes can dry out the skin and trigger flare-ups. Irritants like harsh soaps, detergents, and fragrances can also provoke eczema symptoms. Allergens, including dust mites, pet dander, and pollen, are known to trigger eczema in sensitive individuals. Certain fabrics, particularly synthetic materials or wool, can irritate the skin and exacerbate symptoms. Sweat and excessive moisture on the skin can also lead to eczema flares, making it essential to maintain proper skin hygiene without over-cleansing.
How does eczema affect different parts of the body?
Eczema can manifest differently depending on the affected body part. On the face, it often appears as red, scaly patches, particularly around the eyes and mouth. Scalp eczema may cause dandruff-like flaking and itching. On the hands, eczema can lead to dry, cracked skin, especially on the fingers and palms. Eczema on the body typically presents as itchy, red patches in the creases of elbows and knees. In infants, eczema commonly affects the cheeks, scalp, and limbs. Understanding these variations is crucial for targeted treatment and management strategies.
When should someone with eczema seek professional medical help?
While mild eczema can often be managed at home, certain situations warrant professional medical attention. If over-the-counter treatments fail to provide relief after a few weeks, it’s time to consult a dermatologist. Seek immediate medical help if you experience severe itching that interferes with sleep or daily activities, if your skin becomes painful or develops signs of infection (such as oozing, crusting, or fever), or if eczema spreads to new areas of the body. Additionally, if eczema significantly impacts your quality of life or mental health, professional intervention can provide much-needed support and advanced treatment options.
Which dermatologist-recommended treatments have proven effective in managing eczema over time?
Dermatologists employ a range of treatments to manage eczema effectively. Topical corticosteroids remain a cornerstone of eczema treatment, reducing inflammation and itching. For long-term management, non-steroidal topical medications like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus have shown efficacy without the side effects associated with prolonged steroid use. Oral antihistamines can help control itching, especially at night. For severe cases, systemic medications such as cyclosporine or methotrexate may be prescribed. Phototherapy, using controlled exposure to UVB light, has also proven effective for some patients. Newer biological treatments, like dupilumab, target specific pathways in the immune system and have shown promising results in managing moderate to severe eczema.
What lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage eczema symptoms?
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing eczema. Maintaining proper skin hydration is essential; use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers regularly, especially after bathing. Opt for lukewarm showers or baths and pat the skin dry gently. Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is key to preventing flare-ups. Wear soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid scratchy materials. Manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or meditation. Humidifiers can help maintain optimal indoor humidity levels, particularly in dry climates. Some individuals find relief with natural remedies like colloidal oatmeal baths or applying coconut oil, although it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying new treatments.
Eczema management requires a multifaceted approach combining medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and consistent skin care. By understanding the triggers and implementing effective management strategies, individuals with eczema can significantly improve their skin health and overall quality of life. Remember, what works best can vary from person to person, so it’s important to work closely with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.